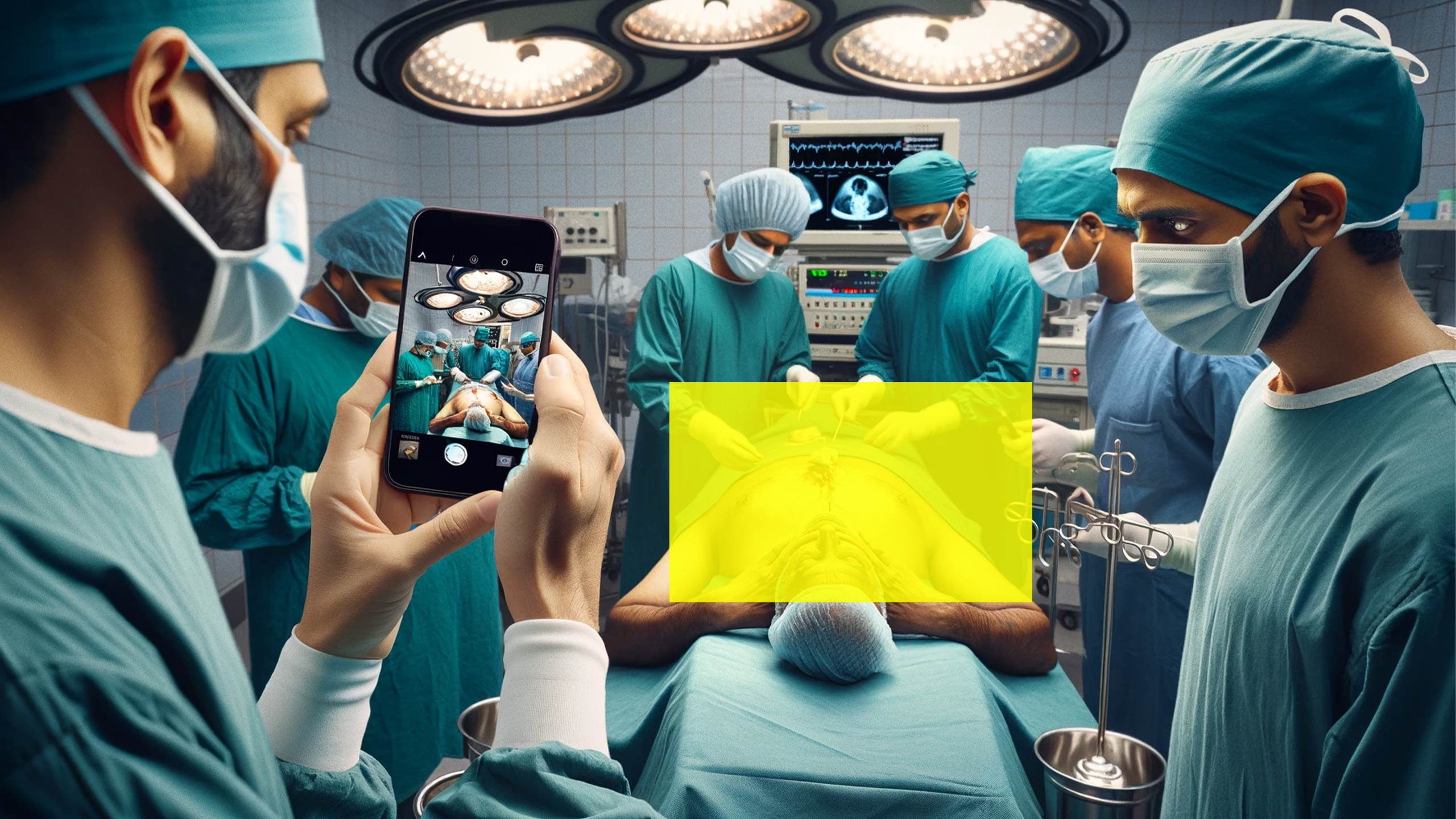
In India, capturing photographs of patients in the operating theater (OT) without obtaining prior consent can lead to a range of disciplinary actions against medical practitioners. The severity of these consequences varies depending on the gravity of the offense and the relevant regulatory framework. This article explores the ethical and legal implications of this practice and offers a comprehensive breakdown of the potential repercussions.
Ethical Breaches:
• Violation of Patient Confidentiality: By photographing patients in a vulnerable OT environment without their consent, doctors breach the fundamental principles of patient privacy and confidentiality. Such actions directly contravene the ethical guidelines established by the Indian Medical Council (MCI).
• Professional Misconduct: The act can be classified as professional misconduct under the Indian Medical Council Regulations of 2002. This classification carries a spectrum of penalties, including warnings, censure, temporary suspension, or even permanent removal from the medical register.
Legal Ramifications:
• Patient Right to Privacy: While there isn't a specific Indian law addressing this issue, the right to privacy is enshrined in the Indian Constitution. Unauthorized photography without consent may be considered an invasion of privacy, and patients could seek legal recourse through civil courts.
• Information Technology Act, 2000: Sharing or publishing such images without consent could potentially violate Section 66E of the Information Technology Act, 2000, dealing with the publication of obscene materials. The consequences may include imprisonment for up to three years and a fine.
Disciplinary Process:
• Filing Complaints with State Medical Council: Patients have the option to file complaints with the state medical council where the doctor is registered. These councils will conduct investigations and initiate disciplinary proceedings against the doctor if warranted.
• Pursuing Civil Lawsuits: Patients also have the legal avenue to initiate civil lawsuits against the doctor to seek compensation for damages resulting from the invasion of their privacy.
Factors Influencing Severity:
• Intent: The severity of the consequences may depend on the doctor's intent behind taking the photographs. If they were taken for educational purposes and kept confidential, the punishment might be less severe compared to photographs taken for personal gain or public sharing.
• Harm Inflicted: If patients suffered mental distress or damage to their reputation due to the photographs being shared, the legal and professional consequences could be more severe.
Recommendations:
• Prioritize Informed Consent: Doctors should always seek informed consent from patients before capturing any photographs or videos in a medical setting, explaining the purpose and usage of such images.
• Maintain Patient Anonymity: Ensure that only relevant body parts are captured in the images, and the patient's identity remains confidential.
• Secure Storage and Authorized Sharing: Store and access the images securely, sharing them only with authorized personnel for approved medical purposes.
It is essential to recognize that taking photographs in the OT without consent represents a profound breach of patient trust, carrying significant legal and professional repercussions. Doctors must prioritize patient privacy and adhere to informed consent procedures to maintain the highest ethical and legal standards in healthcare."
What disciplinary action can be taken against a doctor in India for taking patient pictures in OT without prior consent?
..











Recent comments
Latest Comments section by users
Guest
Dec 27, 2023
Only two things can prevent legal problems , consent to take pics and keeping identity of person secret/hidden.